Land Rover Discovery: Selective Catalyst Reduction (SCR) Components - EU6 only
Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) tank module
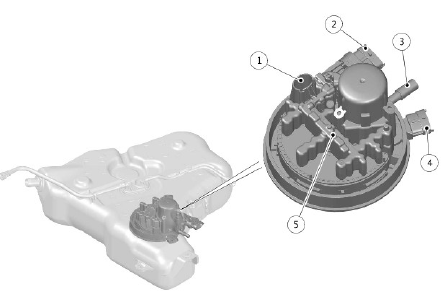
- Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) level sensor
- Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) tank module electrical connection
- Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) pressure line connection
- Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) injection pump electrical connection
- Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) heater element
The DEF tank module is located at the bottom of the DEF tank. The DEF tank module includes a DEF level and temperature sensor and a heater element to defrost the DEF in extreme cold climates.
The DEF level sensor is an ultrasonic device located in the DEF tank module, which sends the DEF level value to the ECM via PWM signals. The NTC temperature sensor measures the temperature of the fluid in the DEF tank.
Similar to the ultrasonic DEF Level sensor, the temperature sensor transmits the initial temperature signal to an evaluation unit in the tank module, where the signal is converted into a PWM signal and sent to the ECM for processing.
The heater element is a Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) type heater.
Under normal operation the maximum current is 6A. The heater element is designed to defrost the DEF in extreme cold climates. The element is a PTC heater that is intrinsically safe to operate. A feature of this design is that the current drawn from the electrical power supply reduces as the temperature of the element increases.
The DEF tank module receives a 12V power supply from a DEF relay located in the Rear junction Box (RJB). The DEF relay is controlled by the ECM via power supplied from the ECM relay in the Engine Junction Box (EJB).
The ECM controls the DEF injection pump which comprises two solenoid pumps within the DEF tank. One pump supplies pressurized DEF to the DEF injector. The second pump purges DEF from the DEF injector supply line to prevent freezing in cold climates. Both pumps are controlled by a ground connection from the ECM.
The DEF tank module also supplies a controlled ground for the DEF fluid line heater. The DEF line heater receives a power supply from the DEF heater control unit and provides heating of the DEF as it passes from the DEF tank to the DEF injector in cold conditions.
Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) Heater Control Unit
The DEF heater control unit is located in the luggage compartment. The control unit receives a permanent 12V battery supply via the Battery Junction Box (BJB) and the RJB.
The DEF heater control unit provides current information for each heater power stage on a private Controller Area Network (CAN) bus to the ECM.
Any faults detected are stored in the ECM fault memory and can be retrieved with an approved diagnostic system.
The DEF line heater receives a power supply from the DEF heater control unit and provides heating of the DEF as it passes from the DEF tank to the DEF injector in cold conditions.
Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) Injector
.jpg)
The DEF injector is located in the exhaust system, downstream of the Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) and delivers a metered amount of DEF into the exhaust pipe.
The DEF injector works at high pressures to provide complete atomization of the injected DEF. This ensures the Selective Catalyst Reduction (SCR) catalytic converter performs at its optimum performance.
The DEF injector is activated by a PWM signal, controlled by the ECM. A signal duty cycle of 3.33 - 4 Hz determines the opening duration of the injector. The injector is designed to operate at a nominal operating pressure of 4.4 and 8.6 bar (64 and 125 psi).
Heat, generated by the exhaust system, is dissipated through the injector by cooling fins built into the body of the injector.
Selective Catalyst Reduction (SCR) sensor and module
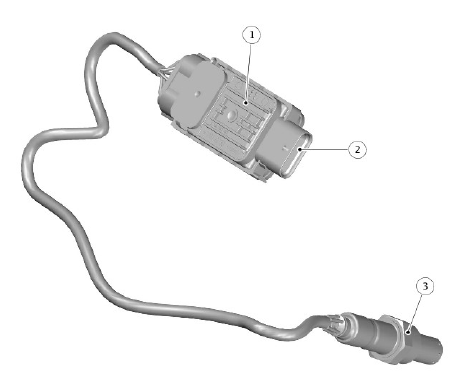
- Post - selective catalyst reduction (SCR) nitrogen oxide (NOx) sensor control module
- Electrical connection
- Post - selective catalyst reduction (SCR) nitrogen oxide (NOx) sensor
The Post - selective catalyst reduction (SCR) nitrogen oxide (NOx) sensor is located in the exhaust pipe downstream of the SCR catalytic converter. The NOx sensor comprises a sensor element attached to a dedicated control module with a hardwired connection.
The sensor and the control module are replaced as an assembly. The NOx sensor is an evolution of the wide band oxygen sensor. The sensor element is constructed from special ceramics and contains two oxygen density detecting chambers that work together to determine the NOx concentration in the exhaust gas. The control module sends a message via the Private CAN bus to the ECM for monitoring the effectiveness of the SCR system.

