Land Rover Discovery: Exhaust - Ingenium i4 2.0l Diesel Selective Catalyst Reduction / Diagnosis and Testing
COMPONENT LOCATION
.jpg)
- Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) filler assembly
- Engine Control Module (ECM)
- Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) tank
- Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) tank module
- Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) heater control unit
- Post - Selective Catalyst Reduction (SCR) nitrogen oxide (NOx) sensor
- Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) injector
- Selective Catalyst Reduction (SCR) catalytic converter
- Nitrogen oxide (NOx) sensor control module
OVERVIEW
The Selective Catalyst Reduction (SCR) system is an exhaust gas aftertreatment solution used to reduce the nitrogen oxides within the exhaust gas.
For this purpose, a specified amount of Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) is injected into the exhaust system, downstream of the DPF. The injected DEF into the exhaust system is converted to ammonia (NH3) and carbon dioxide (CO2). The resulting ammonia (NH3) is used within a special catalyst in the exhaust stream. The resulting reaction converts the unwanted nitrogen oxides (NOx) into harmless nitrogen (N2) and water (H2O) vapor.
DESCRIPTION
DIESEL EXHAUST FLUID (DEF)
Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) is a pure, odorless, colorless, synthetically manufactured, 32.5% aqueous solution of urea, used for the aftertreatment of exhaust gases in a Selective Catalyst Reduction (SCR) catalytic converter.
The SCR catalytic converter can be contaminated by low quantities of metals and thus the quality of the DEF fluid is held to closely controlled standards. DEF cannot be substituted by urea used in agriculture or diluted with any other fluid.
DEF is not categorized as a dangerous substance, it is non-flammable and non-toxic, and there is no danger in the event of spills. DEF can be stored on board vehicles, despite the limitation that it crystallizes at temperatures below -11ºC (12ºF).
In Europe, DEF is also known as AdBlue, the fluid is specified by ISO22241.
DIESEL EXHAUST FLUID (DEF) TANK
.gif)
The Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) tank is blow molded from High Density Polyethylene (HDPE). The tank is located under the right side of the fuel tank and it is secured to the underside of the vehicle in common with the fuel tank by the fuel tank support strap and a bolt secures the DEF tank to the rear left side member. The DEF tank contains the DEF tank module which is welded into the tank, and supplied as a unit. An additional shield protects the DEF tank module. The protection shield is attached to the DEF tank and the fuel tank heatshield with four screws. The tank includes a 12% unusable volume to protect the internal components as a result of fluid expansion under freezing conditions.
If the ambient temperature falls below -11ºC (12ºF), the DEF will freeze in the DEF tank, this will provide difficulty with the refill procedure. In order to thaw the DEF in the DEF tank, place the vehicle in a warm place for up to 2 hours before attempting to refill the tank.
The volume of the DEF tank is different on all JLR products, but has been designed so that refills are minimized outside of the vehicle service intervals.
When the vehicle consumes more DEF than anticipated, for example extended vehicle use in extreme temperatures, 'at altitude' or aggressive drive cycles, a warning message will be displayed in the Instrument Cluster (IC) message center to add DEF to the tank.
DIESEL EXHAUST FLUID (DEF) TANK MODULE
.gif)
- Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) level sensor
- Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) tank module electrical connection
- Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) pressure line connection
- Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) injection pump electrical connection
- Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) heater element
The Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) tank module is located at the bottom of the DEF tank. The module is welded into the tank and can only be replaced as a complete assembly. The DEF tank module includes a life-time fit filter, a fluid level and temperature sensor and a heater element to defrost the DEF in extreme cold climates. The DEF level sensor is an ultrasonic device located in the DEF tank module, which sends the DEF level value to the Engine Control Module (ECM) via Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) signals. The ultrasonic cone angle is +-10º and the readings are most accurate when the vehicle is stationary and on level ground.
The heater element is a Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) type heater, which provides safe operation to the system. Increased heater element temperature results in decreased current drawn from the DEF heater control module, which actuates the power supply of the heater element. Under normal operation the maximum current is 6A.
The DEF tank module has a fused power supply from the Battery Junction Box (BJB). The ECM controls the power supply of the DEF tank module via the DEF control relay located in the Rear Junction Box (RJB).
DIESEL EXHAUST FLUID (DEF) INJECTION PUMP

The Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) tank module comprises a DEF injection pump which is an assembly of two solenoid pumps. The DEF injection pump provides 6.5 bar operating pressure. The 6.5 bar pressure is required to maintain the complete DEF atomization in the exhaust gas. The purge pump is used to purge the DEF from the DEF pressure line at engine shut-down to prevent freezing in the DEF injector at low temperatures. The pumps have a fused power supply from the Rear Junction Box (RJB). The ECM controls the ground connection of the pumps individually via hardwired connections.
DIESEL EXHAUST FLUID (DEF) LINE
.gif)
The Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) line provides hydraulic connection between the DEF injection pump and the DEF injector. The DEF line is manufactured from a plastic material which is specifically designed for use with DEF. A copper based resistor wire DEF line heater is installed within the DEF line with an electrical connector. The DEF line heater enables electrical heating of the DEF at low-ambient temperatures. The DEF line heater has hardwired connections to the DEF heater control unit, which actuates the power supply for the heater element, controlled by the ECM via the Private Controller Area Network (CAN) bus.
DIESEL EXHAUST FLUID (DEF) INJECTOR
.gif)
The Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) injector is located in the exhaust system downstream of the catalytic converter and it is secured to the S-shaped exhaust pipe with a clamp. Due to the position of the injector on the Sshaped exhaust pipe, the DEF is injected axially to the exhaust gas flow direction ensuring the DEF is mixed well and distributed evenly within the exhaust gas. The DEF injector consists of an injector and a passive cooling heat sink to protect the injector from overheating due to the high exhaust temperatures.
The DEF injector works at high pressures to obtain the complete atomization of the injected DEF, this ensures the SCR catalytic converter is working to its optimum performance. The DEF injector is controlled by the ECM with PWM signals.
DIESEL EXHAUST FLUID (DEF) HEATER CONTROL UNIT
.gif)
The Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) heater control unit is located on the left side of the luggage compartment, behind the side trim panel. The heater system enables rapid SCR system operation in the event of frozen DEF and ensures an adequate quantity of defrosted DEF is available at all operating points.
The DEF heater control unit has a fused power supply from the RJB and it receives an ignition signal from the ECM relay located in the BJB. Operation of the ECM relay is controlled by the ECM.
The DEF heater control unit has hardwired connections to the DEF tank module and the DEF line heater. If the ambient air temperature is below -7ºC (19.4ºF), the ECM switches on the DEF heater control unit via the Private CAN bus. The DEF heater control unit energizes the DEF tank module heater element and the DEF line heater. The DEF heater control unit has on-board diagnostics to detect and report faults to the ECM via the Private CAN bus.
NITROGEN OXIDE (NOX) SENSOR
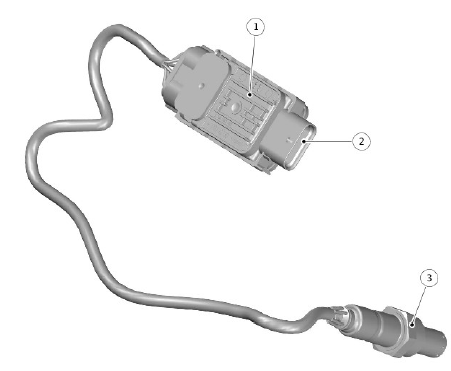
- Post - selective catalyst reduction (SCR) nitrogen oxide (NOx) sensor control module
- Electrical connection
- Post - selective catalyst reduction (SCR) nitrogen oxide (NOx) sensor
The Post - selective catalyst reduction (SCR) nitrogen oxide (NOx) sensor is located in the exhaust pipe downstream of the SCR catalytic converter. The NOx sensor comprises a sensor element attached to a dedicated control module with a hardwired connection.
The sensor and the control module are replaced as an assembly. The NOx sensor is an evolution of the wide band oxygen sensor. The sensor element is constructed from special ceramics and contains two oxygen density detecting chambers that work together to determine the NOx concentration in the exhaust gas. The control module sends a message via the Private CAN bus to the ECM for monitoring the effectiveness of the SCR system.
OPERATION
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM - SELECTIVE CATALYST REDUCTION (SCR) SYSTEM
.jpg)
- Engine Control Module (ECM)
- Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) tank with Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) tank module
- Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) injection pump
- Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) line
- Post - Selective Catalyst Reduction (SCR) nitrogen oxide (NOx) sensor
- Selective Catalyst Reduction (SCR) catalytic converter
- Mixer plate
- Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) injector
- Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF)
- Catalytic converter
- Engine
The SCR catalytic converter reaches the operating temperature at 150 ºC (302ºF). The temperature of the exhaust gas is measured by the post DPF exhaust gas temperature sensor, which is connected to the ECM.
The DEF injection pump supplies the DEF from the DEF tank at a pressure of 6.5 bar to the DEF injector via the heated DEF line. The DEF injector is controlled with a Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) signal by the ECM.
The injected DEF is carried along by the exhaust gas flow and is evenly distributed in the exhaust gas by the mixer plate. The mixer plate is located in the exhaust pipe upstream of the SCR catalytic converter and downstream of the DEF injector. After the injection, the DEF is converted into ammonia (NH3) and carbon dioxide (CO2) during chemical reactions.
In the SCR catalytic converter, the ammonia (NH3) reacts with the nitrogen oxides (NOx) to produce nitrogen (N2) and water (H2O) vapor. The SCR system's efficiency is registered by the post SCR NOx sensor.
In order to optimise the SCR system's efficiency, the correct amount of ammonia (NH3) is required in the exhaust gas. The ECM achieves this by operating in two modes:
- Storage mode
- On-line mode
For example, storage mode will operate during low speed driving condition; the on-line mode will operate at high speed driving condition.
STORAGE MODE
When the system operates in storage mode, the ammonia (NH3) is stored on the SCR catalytic converter and used as a function of the NOx feed. In this mode, the objective of the control system is to ensure that a predetermined amount of NH3 is available on the SCR catalytic converter at any given time. As a consequence, it may be difficult to diagnose dosing system problems when the system is in storage mode.
ON-LINE MODE
When the system operates in on-line mode, the NOx is measured by the pre-SCR NOx sensor (or the model value) and the amount of ammonia (NH3) is injected as a function of the NOx feed. In this mode, the dosing system is 'easy' to diagnose if it is functioning correctly as the pulses from the DEF injector are frequent.
WARNING MESSAGES
It is a legal requirement for the driver to be informed of SCR system faults. If the performance of the SCR system is reduced a message will be displayed in the Instrument Cluster (IC) message center. There are three possible routes to receive a fault message on the IC:
- Low DEF volume in the tank
- Incorrect DEF quality supplied to the SCR System
- Efficiency of the SCR System is reduced in the event of a system fault.
In case of low DEF level, a warning is given 800km (497 miles) ahead of any vehicle restriction in order to allow time to visit an authorized Land Rover dealer to refill the DEF tank. If the DEF fluid is not replenished within this distance, and the engine is turned off, the vehicle will fail to start. In this event customers can use two standard size refill bottles as a short term solution to restart the vehicle, a complete refill of the DEF tank will still be required by an authorized Land Rover dealer.
INPUT/OUTPUT DIAGRAM
.jpg)
A = HARDWIRED; AL = PULSE WIDTH MODULATION (PWM); U = PRIVATE CONTROLLER AREA NETWORK (CAN) BUS.
- Engine Control Module (ECM)
- Post-Selective Catalyst Reduction (SCR) nitrogen oxide (NOx) sensor control module
- Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) heater control unit
- Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) tank module heater element
- Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) line heater
- Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) injection pump
- Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) injector
- Ground
- Power supply
- Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) level sensor
- Post Selective Catalyst Reduction (SCR) NOx sensor
Exhaust - Ingenium i4 2.0l Diesel / Specifications
All vehicles:.jpg)
With Diesel exhaust fluid system:
.jpg)

