Land Rover Discovery: Crankshaft
.jpg)
- Thrust washers (2 off)
- Timing chain drive sprocket
- Pin - dual mass flywheel (manual transmission) or drive plate (automatic transmission) location
- Dynamic balancer drive gear
- Lower main bearings (5 off)
- Alignment roll pin - Crankshaft pulley / mass damper location
- Crankshaft pulley / mass damper location
- Crankshaft
- Upper main bearings (5 off)
The crankshaft is manufactured from forged carbon steel C38 with induction hardened main bearing journals. The fillets of the main journals are fillet rolled to improve the strength of the crankshaft.
A five counterweight design has been used to balance bearing loads to give class-leading vibration levels.
An oil groove in the upper half of each main bearing transfers pressurized engine oil into the crankshaft for lubrication of both the main bearings and connecting rod bearings. The crankshaft assembly comprises the bare crank and a dynamic balancer shaft system drive gear. This gives direct drive at a ratio of 2:1 of the two counter-rotating dynamic balancer shafts.
Two individual thrust washers are located on either side of the central main bearing journal panel of the cylinder block to control crankshaft end float.
CRANKSHAFT INSTALLATION
.jpg)
- Main bearing cap bolts
- Front main bearing cap
- Main bearing caps (3 off)
- Rear main bearing cap
- Orientation arrow
The crankshaft is retained in position by five main bearing caps that are manufactured from sintered steel. Each individual main bearing cap has a numbered identification (1-5) and an arrow to ensure correct location and orientation; the arrow must face towards the front of the engine.
There are a number of grades of main bearing available. Each main bearing shell is color coded and inkjet marked with a number on the running face of the bearing. The crankshaft is laser etched with a string of five alpha characters in the order of crankshaft main bearing journals 1-5 and a data matrix code containing the same data. The correct main bearing shells are selected with reference to a selection chart in order to achieve optimum running clearances.
For additional information, refer to: Specifications (303-01B Engine - INGENIUM I4 2.0L Diesel, Specifications).
The main bearing shells in the cylinder block have a central hole and an internal groove to allow for main bearing journal lubrication. The main bearing shells in the main bearing caps are plain with no hole or internal groove.
CRANKSHAFT PULLEY / MASS DAMPER
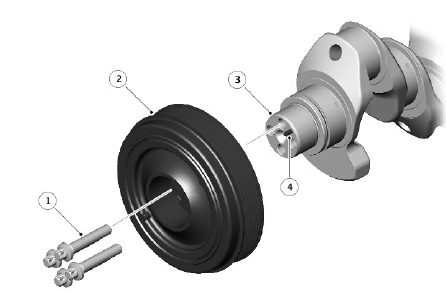
- M10 bolt (4 off)
- Crankshaft pulley / mass damper / torsional isolator
- Crankshaft
- Alignment roll pin
At the front of the crankshaft is a crankshaft pulley/mass damper which drives the primary drive belt for the ancillary components. A tuned torsional mass damper is incorporated into the crankshaft pulley which dampens vibration in the crankshaft produced by the combustion process. Each time a cylinder fires, torque is applied to the crankshaft via the pistons and connecting rods. The crankshaft deflects in reaction to the torque which creates a vibration when the torque is dissipated. The mass damper absorbs the vibration reducing fatigue damage to the crankshaft.
A torsional isolator is incorporated into the crankshaft pulley to provide isolation and reduce primary drive belt loads to the ancillary components.
The crankshaft pulley is located over an alignment roll pin that is press-fitted into the crankshaft nose. Four bolts, that are torqued to yield, secure the crankshaft pulley to the crankshaft. An O-ring seal provides a seal between crankshaft pulley hub bore and the crankshaft nose outer diameter to prevent oil leakage during engine running conditions.
The crankshaft pulley has a timing mark that, when aligned to a corresponding timing feature on the front cover assembly, aligns the crankshaft to 50º After Top Dead Center (ATDC) on Cylinder 1. The crankshaft pulley/mass damper assembly is not a serviceable component and must not be disassembled.
DRIVE PLATE / DUAL MASS FLYWHEEL
.jpg)
- Drive plate - automatic transmission
- Dual mass flywheel - manual transmission
- Reluctor ring
- Ring gear - Tandem solenoid starter (TSS) motor
- M10 bolt (8 off)
The drive plate or dual mass flywheel is located at the rear of the crankshaft.
A dowel in the crankshaft ensures that drive plate or dual mass flywheel is indexed correctly.
Eight sealant patched bolts secure the drive plate or dual mass flywheel to the crankshaft. The bolts can only be used once and must be replaced if removed. Before replacement bolts are used, the holes must be dry and free from oil.
The drive plate or dual mass flywheel has three functions; to transfer drive from the crankshaft to the transmission, to transfer drive from the starter motor to the crankshaft and to provide the engine management system with crankshaft speed and position via a reluctor ring and a Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor.
The reluctor ring has 58 teeth with 2 teeth missing to provide a gap. A Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor is located in the lower timing chain cover and measures rotational speed and position as the reluctor ring rotates.
Drive Plate
The drive plate is used for automatic transmissions only.
The drive plate is a fabrication, which comprises a formed steel starter ring gear which is attached to the drive plate and reluctor ring. The two components are held together as one assembly by a form of clinching known as Tog-L-Loc.
The reluctor ring has a service tool slot used during engine service procedures. The drive plate incorporates a steel starter ring gear which enables the starter motor to start the engine.
Four holes in the drive plate provide for the attachment of the automatic transmission torque converter to transfer drive from the crankshaft to the automatic transmission.
Dual Mass Flywheel
The Dual Mass Flywheel (DMF) is used for manual transmissions only.
The dual mass flywheel comprises two main components; the primary side which is attached to the engine crankshaft and the secondary side to which the clutch cover assembly is attached. The primary and secondary side are divided by a multi-spring damping system and centrifugal pendulum vibration damper. This provides a multi-stage characteristic curve designed to ensure optimal vibration isolation.
The primary side of the dual mass flywheel is a pressed steel fabrication and incorporates a reluctor ring.
The secondary side of the DMF is cast steel onto which the clutch cover assembly is located on dowels and secured with six bolts. The secondary side has the smooth friction surface on which the driven plate friction material engages.
For additional information, refer to: Clutch - AWD (308-01 Clutch, Description and Operation).

